This article is a comprehensive guide that explains IVF frozen embryo transfer, when a couple should consider it, how to prepare for it, what to expect from it, how long the procedure takes, its step by step process, success rate, and common symptoms along with valuable tips for success.
IVF Frozen Embryo Transfer
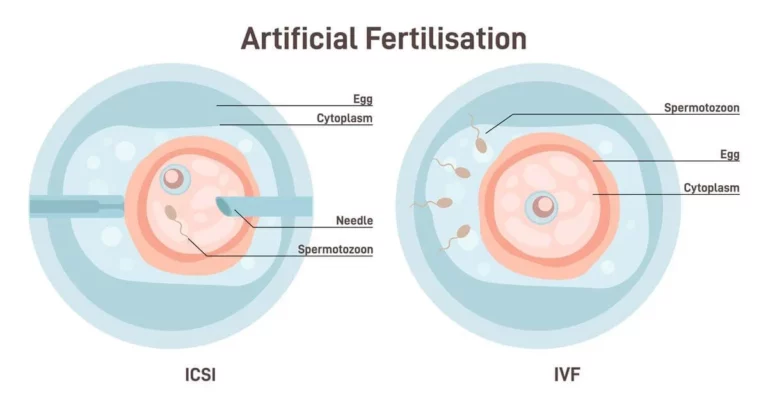
Frozen Embryo Transfer, better known by its abbreviation FET, is an advancement in the in-vitro fertilization (IVF) technique. Unlike conventional IVF where fresh eggs are collected and fertilized for implantation, frozen embryo transfer involves the use of frozen embryos (fertilized eggs) instead, usually from the patient’s earlier IVF cycles.
IVF frozen embryo transfer is probably a good pregnancy treatment if conventional IVF or other fertility treatments do not help. But, there are few things you must be aware of beforehand.
Increase your pregnancy chances with Nory Ovulation Kit
Who is a good candidate for Frozen Embryo Transfer?
- Women who are incapable of conceiving due to irregular ovulation cycles.
- Women who have ovulation complications such as ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS). Pregnancy can worsen OHSS and it can be avoided by freezing the embryos and postponing the implantation until the OHSS is treated.
- Women undergoing certain treatments such as for cancer, that increase the risk of potentially damage the embryo and affect the baby.
- Women with higher progesterone level. High progesterone levels during embryo transfer can lower the likelihood of pregnancy. In such cases, eggs can be fertilized and frozen to use later when progesterone levels are managed.
- Any woman who does not want to become pregnant right now, but wants to ensure that fertility decline throughout aging does not complicate her pregnancy. In such a case, her eggs are collected, fertilized and frozen in her peak reproductive years, to be used at a later time.
What happens to eggs during frozen embryo transfer?
Before eggs are frozen, they are incubated until they become blastocyst (day 5) embryos. They are then frozen and collected in vials. In some cases, eggs are also frozen right after fertilization (day 1) or in their cleavage stage (day 3).
During the frozen embryo transfer procedure, factors that determine the number of frozen embryos to be thawed and used for transfer are:
- Woman’s age
- Quality of embryos, and
- Number of embryos collected and frozen
The fertility doctor always ensures that the number of embryos transferred during the FET cycle gives you the highest possibility of a successful pregnancy, and the lowest risk of multiple gestation (become pregnant with more than one baby).
Are there any complications associated with FET?
Yes, there are a few complications associated with frozen embryo transfer. But, the likelihood of developing these complications are very uncommon. These complications include:
- Multiple gestation: The risk of being pregnant with multiple babies at a time. Multiple gestation also increases the chances of preterm labor, premature birth, higher risk of birth defects.
- Health problems to mother: Undergoing the administration of several drugs can also cause some health problems such as blood clotting, gestational diabetes or preeclampsia to the mother. However, these problems are manageable.
- Delayed embryo transfer: In some cases, endometrium can take longer to thicken for transfer than expected. This will postpone the embryo transfer date and you may have to undergo hormone administration for longer.
Types of IVF Frozen Embryo Transfer
There are two common types of IVF frozen embryo transfer approaches that are:
Hormone based FET
Hormone based IVF-FET is the most common FET approach that involves administration of certain drugs to control ovulation activity and prepare the endometrium to accept the transferred embryo. Fertility clinics prefer hormone based FET because it is easily manageable and women with ovulation complications can also become pregnant by getting additional medicinal help.
Natural FET
Unlike hormone based FET where ovulation is managed by certain drug administration, natural FET involves embryo transfer depending on your natural ovulation cycle. However, you may be given a hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) shot to induce ovulation and progesterone administration after the embryo transfer to support pregnancy.
IVF Frozen Embryo Transfer Timeline

IVF frozen embryo transfer timeline may differ depending on whether you are undergoing the complete IVF and FET cycle, or you have had your eggs collected and embryos frozen before.
FET cycle along with complete IVF process including ovarian stimulation, egg retrieval, sperm collection, fertilization and egg incubation will take around 6-8 weeks. Whereas, frozen embryo transfer alone including hormone administration, thawing and embryo transfer will only require around 3 weeks.
IVF Frozen Embryo Transfer Process: Step by Step
As mentioned above, IVF-FET timeline can differ depending on if the patient is undergoing the complete IVF and FET cycle, or the FET cycle alone. If a patient has got his eggs collected, fertilized and frozen earlier, her frozen embryo transfer process step by step will be as following:
Step 1: Administering Hormones
Before thawing the frozen embryos and transferring them, you will be administered under certain hormones to control your ovarian activity and prepare your uterus to accept the embryo. First, the fertility doctor can inject Lupron (leuprolide) or prescribe birth control pills to manage your ovarian activity for about 1-2 weeks.
After that, you will be administered under estradiol. Estradiol will prepare your endometrium to accept the transferred embryo by thickening it.
Step 2: Performing Tests
After about 2 weeks of administering estradiol, a blood test and transvaginal ultrasound will be performed to determine if estradiol levels are good and endometrium has the right thickness for the embryo transfer.
If estradiol is at a good level and endometrium is thick enough, the fertility doctor will further administer progesterone hormone and prepare for frozen embryo thawing and implantation. Moreover, sometimes a fertility doctor can also administer Medrol (a steroid) for about a week to help with embryo transfer.
Step 3: Transferring Embryos
Finally, the frozen embryos will be thawed and prepared for implantation. The healthy embryos will then be transferred in the uterus. Additionally, you will be asked to continue taking estradiol and progesterone until your fertility doctor says otherwise, usually until you are at least 10-12 weeks pregnant.
Step 4: Testing for Pregnancy
Pregnancy test after IVF frozen embryo transfer is usually done 2 weeks post embryo implantation. Your fertility doctor will perform a hCG blood test to confirm the pregnancy.
Common Symptoms after Frozen Embryo Transfer
You can expect the following common symptoms after IVF frozen embryo transfer. These symptoms usually disappear in a few weeks on their own. If they do not, your doctor can prescribe some medicines.
- Cramps
- Discomfort
- Little bleeding
- Infection due to catheter, in rare cases. Treatable with some antibiotics.
Frozen Embryo Transfer Success Rate

Unlike conventional IVF that has a success rate of about 40% in younger women and about 30-35% in women above the age of 35, IVF with frozen embryo transfer has a comparatively higher success rate.
With IVF-FET in women who are 35 or younger, a success rate is about 50-60% that declines to 20-30% in women over the age of 40.
It is important to note that whether it is conventional IVF, IVF with FET or any other fertility treatment, its success rate gradually declines as the woman ages. It is because of the drop in the woman’s natural reproductive potential. In several IVF cases of women over the age of 35, they cannot get pregnant in their very first cycle, and need to undergo at least 2-3 full cycles to attain pregnancy.
Moreover, other than women’s age, there are some factors that influence success chances of a frozen embryo transfer (FET) cycle. These are:
- How long the couple is experiencing infertility.
- Reason for infertility
- Type of infertility: There are two types of infertility, one is primary infertility (when you have never become pregnant and it is your first time) and another is secondary infertility (when you have had a baby without complications before, but have trouble conceiving now).
- Quality of collected egg and sperm, and quality of the embryos used for implantation.
- Endometrium thickness at the time of implantation.
Frozen Embryo Transfer Tips for Success

When you are undergoing an IVF frozen embryo transfer cycle, it is important that you prepare your body for it and consider tips that could improve your success chances.
Some science-backed valuable tips for FET success include:
Tip 1: Get your diet right
A good diet is made of protein, carbohydrates and fats. All you need is to find a healthy source of each of them. For protein, you can eat lean meat, eggs, chicken and seafood. For carbohydrates, eat whole grains and green vegetables. And, for healthy fats, eat avocados and nuts. Also, make certain that you are eating a good amount of antioxidant-rich foods such as berries, carrots and broccoli.
Tip 2: Get your habits right
Multiple case studies have confirmed that certain habits such as getting quality sleep, avoiding caffeine and alcohol, drinking plenty of water, doing moderate strength-training and cardiovascular exercises, and reducing physical and psychological stress have improved fertility and pregnancy outcomes.
Tip 4: Manage your BMI
BMI stands for body mass index. It is your body weight depending on your age, gender and height. Maintaining an ideal BMI is essential for healthy body functioning, flexibility and mobility. Moreover, it also influences your reproductive health and endometrial receptivity. If you find to have an unhealthy body weight, managing it will help with your fertility and pregnancy.
Tip 5: Take prenatal supplements
Sometimes, a diet cannot fulfil the demand of nutrients your body requires to sustain a healthy pregnancy. So, most fertility doctors recommended taking prenatal supplements, intended for pregnant women only.
The Bottom Line
Having a baby and starting a family is a dream of many couples, but fertility is complicated. Approximately 10-15% couples in India are affected by infertility and have to seek fertility treatments to be able to conceive.
If you have been advised by your fertility doctor to undergo IVF frozen embryo transfer or you are considering it yourself for some reason, going through this article beforehand will be really helpful. The article discussed the IVF-FET treatment, its timeline, step by step process, common symptoms and some valuable tips for success.