Everyone knows about the ultrasound scan aka sonography. It’s a commonly done test to detect and monitor the fetus in a pregnant woman. Sonography is also used to diagnose symptoms/ anomalies in other internal organs like kidneys, breasts, abdomen, etc. But why talk about sonography here? Because it is important to know about ultrasound scan as the transvaginal ultrasound is based on the same principle.
As the name suggests, ultrasound scan uses ultrasound waves to get real-time video/ pictures of any internal organ of the body. A device called ‘transducer’ is moved over the external surface of the body part to be scanned. The transducer first converts electrical energy into sound waves of high frequency which penetrate the surface of the body. The waves strike the internal organ(s) and are thrown back to the transducer which then changes back the waves into electrical signals. A monitor is connected to the transducer which receives these signals and produces images or a video of the internal organ(s).
Now that we know what an ultrasound scan is and how it works, let’s look at TVS ultrasound.
What is Transvaginal (TVS) Ultrasound?
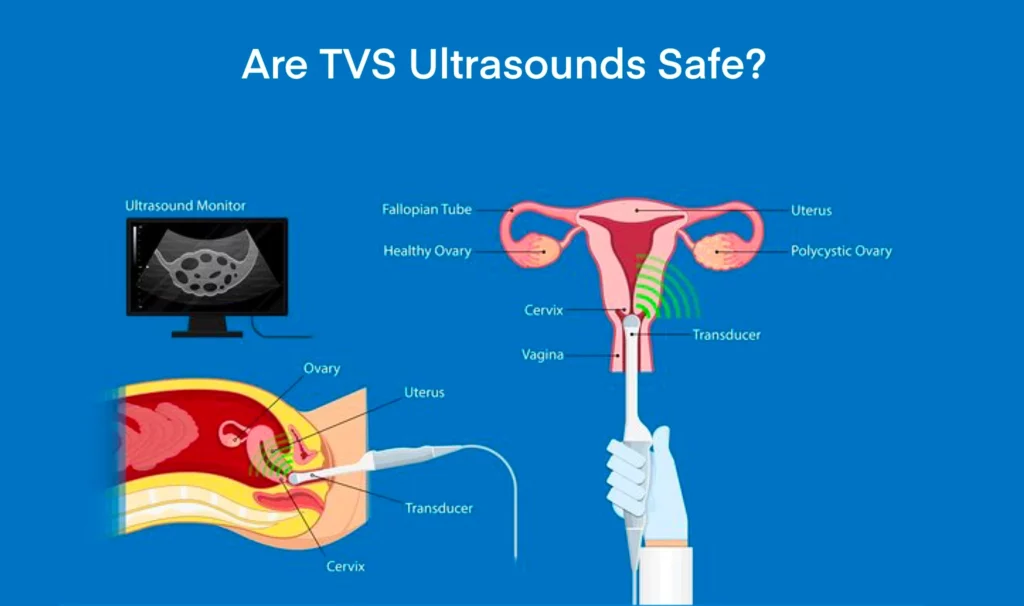
It is a procedure that is conducted for examining the vagina, uterus, ovaries, bladder, and fallopian tubes. Unlike an ultrasound, which is a noninvasive procedure, a transvaginal ultrasound requires the doctor to insert the transducer into the vagina for getting the scan done. Also, as is clear, TVS ultrasound is a subtype of the ultrasound scan test and has a limited scope. It’s only used to detect/diagnose and track the growth of pregnancy or diseases related to the reproductive system.
TVS ultrasound is also known as endovaginal ultrasound because it involves the insertion of a transducer 3-6 cm into the vagina. Doing a transvaginal ultrasound during pregnancy may help:
- Monitor the fetus’ heartbeat
- To predict the delivery date
- Diagnose ectopic pregnancy
- Assess the placenta
- Monitor pregnancies where the risk of miscarriage are high
Therefore, a transvaginal ultrasound pregnancy test can help both the doctor and potential parents in tracking the growth of the fetus. However, there are many other cases where this test can be of immense use:
- To examine an abnormal pelvis or abdomen
- To know the reason for an otherwise mysterious vaginal bleeding
- To inspect and find causes for infertility
- To check for fibroids or cysts in the uterus or ovaries
- To verify that the intrauterine device has been placed correctly
- To check the size and shape of bladder, ovaries, and uterus
- To diagnose endometriosis
What is the Detailed Procedure of a Transvaginal Ultrasound?
When you go for this test, the technician/ doctor will most probably ask you to remove clothes from your lower body and/or wear the hospital gown. You’ll then be asked to lie down on the examination table with your knees bent so that the vagina is easily accessible. The transducer/probe, covered with a condom and coated in lubricating gel will then be slowly inserted into your vagina. The technician/doctor may rotate the probe inside to send the sound waves in all directions for getting a clearer image of the target-organ. The resulting image/video will be visible in the attached screen which may or may not be in your vision. After the doctor or technician is satisfied with the resulting images, he/she will gently take the probe out, clean the area, and ask you to get redressed. The entire procedure would be completed within an hour.
Sometimes, for a more detailed and clear picture, the doctor or technician may opt for an advanced form of TVS ultrasound called SIS (saline infusion sonography). Salt solution makes it easier to see the endometrium. However, note that SIS is not performed on pregnant ladies.
What to Do Before the Test?

No special preparations are needed prior to this test. After you’ve got an appointment, you only need to make sure that you follow your doctor’s instructions of having an empty or partially-filled bladder. Or if they ask you to keep a full bladder (because it pushes the intestines up and gives a clear view of your pelvis), make sure you do so by drinking plenty of water beforehand.
Wear easily removable clothes for convenience.
Lastly, if you are menstruating, you’ll need to remove the tampon/cup/pad you’re wearing.
Is Transvaginal Ultrasound Painful?
Even though it involves the insertion of the transducer inside your vagina, this procedure is not at all painful. The shape of the transducer is made to fit the vagina. Moreover, it is coated in a lubricating gel to ensure a gentle insertion. That being said, some women might find it a little uncomfortable when the technician pushes the device in. Once the procedure is over, you can get back to your daily activities without any problem.
Are TVS Ultrasounds Safe?
Yes, they are pretty safe. This test does not involve the use of any radiation (as in X-ray test) therefore, it’s quite safe. Studies have shown it to be safe for pregnant women as well. If you notice some bleeding after the test, it may be the blood that was collected in the upper part of the uterus. It’s usual for doctors to prescribe the test during the first twelve weeks of pregnancy. Even after that, some doctors might ask for a transvaginal ultrasound as it gives a more detailed report than the normal pregnancy ultrasound test.
How Much Does a Travnsvaginal Ultrasound Cost?

This test is generally not too expensive. Depending on where you live in India, one such test will cost you between Rs.500 and Rs.2000.
When Can We Get the Report?

If the doctor is performing the test himself/herself, chances are you’ll get an immediate report as he/she will look at it and draw conclusions instantly. However, if a technician performs the procedure, the images/videos are sent to a radiologist who reads and interprets them. The report is then sent for the doctor’s use. This might take some hours to days.
Final Words

A transvaginal ultrasound is a type of pelvis ultrasound which differs from the traditional ultrasound in that the former involves the insertion of a transducer into the vagina. It has been found to be of great help in detecting pregnancy or diseases in the reproductive system. Doctors also use it to check the growth and development of a fetus.
It is not dangerous for the mother and/or child as it does not use any radiation. Entire procedure is done with care and light pressure to ensure minimum discomfort. The woman should not experience any pain during the test. You need not take special measures before the test, only follow your doctor’s instructions.
The results are usually either available the same day or within 24 hours. Your doctor will define the future course of action based on your test report.
Lastly, if you feel excessively uncomfortable anytime during the test, you can ask the technician/ doctor to stop the procedure right there. If you do not feel comfortable about the idea of putting the transducer into your vagina, you can always opt for the traditional ultrasound which does not need the insertion. However, know that the TVS ultrasound is a superior technology and ensures better results.