What is fallopian tube blockage? Does it have an effect on your fertility?
In this comprehensive article, we will be trying to explain fallopian tubes, tubal blockage, its signs, reasons, effect on fertility, diagnosis, available treatments, and if it is possible to get pregnant with blocked fallopian tubes.
This article will also include an in-depth description on how you can deal with fallopian tube blockage and attain a healthy pregnancy even while having the condition.
What is a Fallopian Tube?
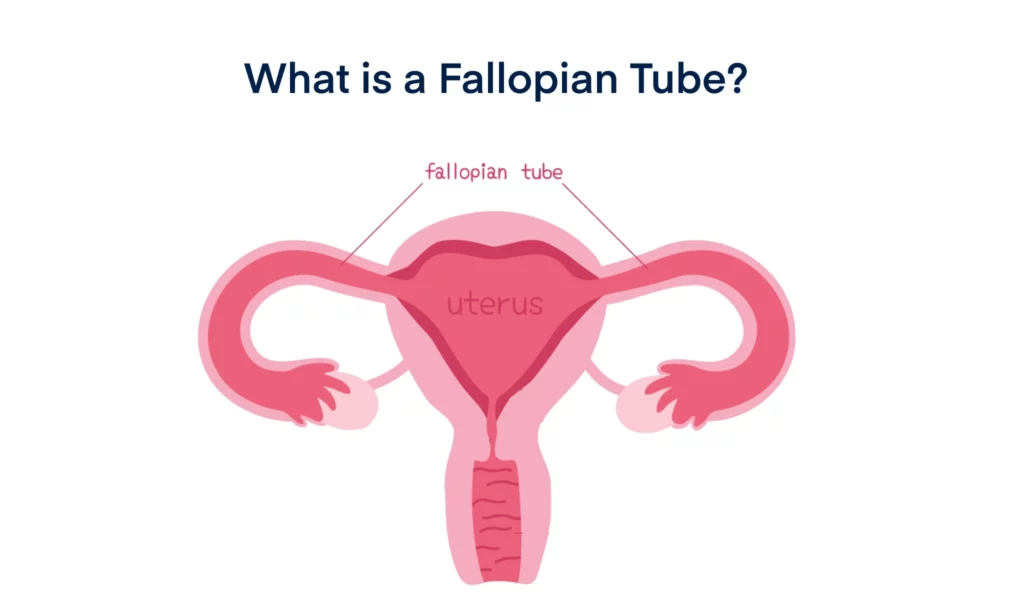
As a part of a female’s reproductive function, fallopian tubes otherwise called uterine tubes or oviducts are a pair of long narrow tubes that connect the ovaries to the uterus. Fallopian tube is the place where sperm fertilizes a woman’s mature egg. Also, the fallopian tubes function as a channel of transport for the fertilized egg to the uterus, towards its further development stages.
In simpler words, when a woman releases a mature egg during her ovulation cycle, the sperm fertilizes the egg inside the fallopian tube. And, after fertilization takes place, the fallopian tube is also the channel of transport that carries that fertilized egg to the uterus, where the egg further develops.
What is Fallopian Tube Blockage?
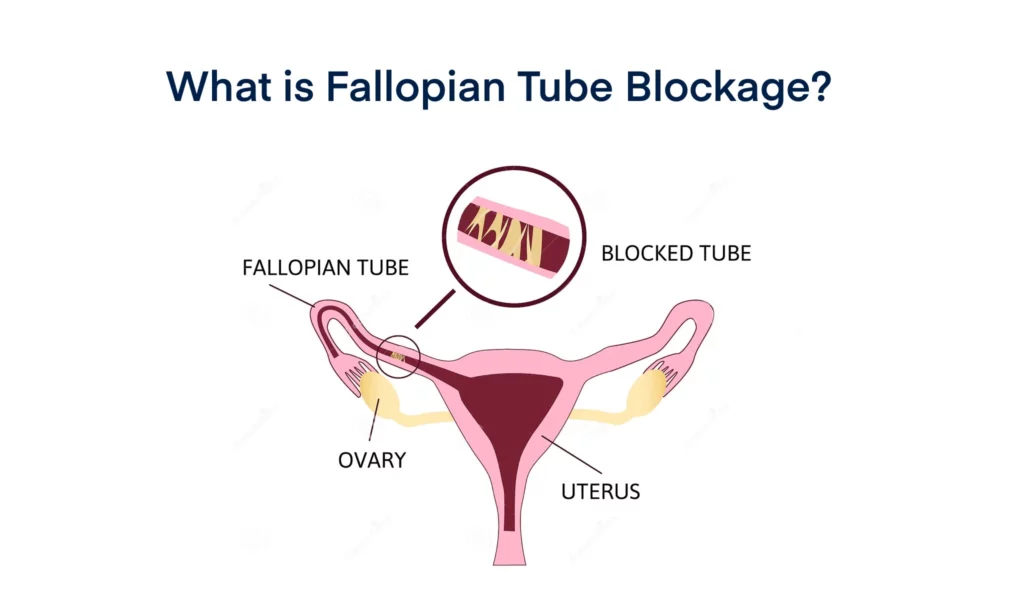
Fallopian tube blockage is a condition in which the male sperm cannot reach the egg for fertilization, often due to some damage or blockage in the fallopian tubes caused by a scarring, infection or adhesion.
Since tubal blockage affects a woman’s reproductive ability by preventing the sperm from reaching the egg, fallopian tube blockage is one of the common reasons for infertility among women.
Signs of Fallopian Tube Blockage
Having blocked fallopian tubes does not generally have any clear symptoms. Women usually do not know about the condition until they have difficulty getting pregnant and visit a fertility doctor.
So, we can say that having trouble getting pregnant can be a sign that you have blocked fallopian tubes. Other than this, tubal blockage can also provoke some side effects such as pelvic or abdominal pain. Moreover, the condition that causes fallopian tube blockage can have its own symptoms. For instance, endometriosis is one of the causes of tubal blockage. And, a woman who has endometriosis struggles with symptoms such as heavy pelvic and abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding.
Reasons of Blocked Fallopian Tubes
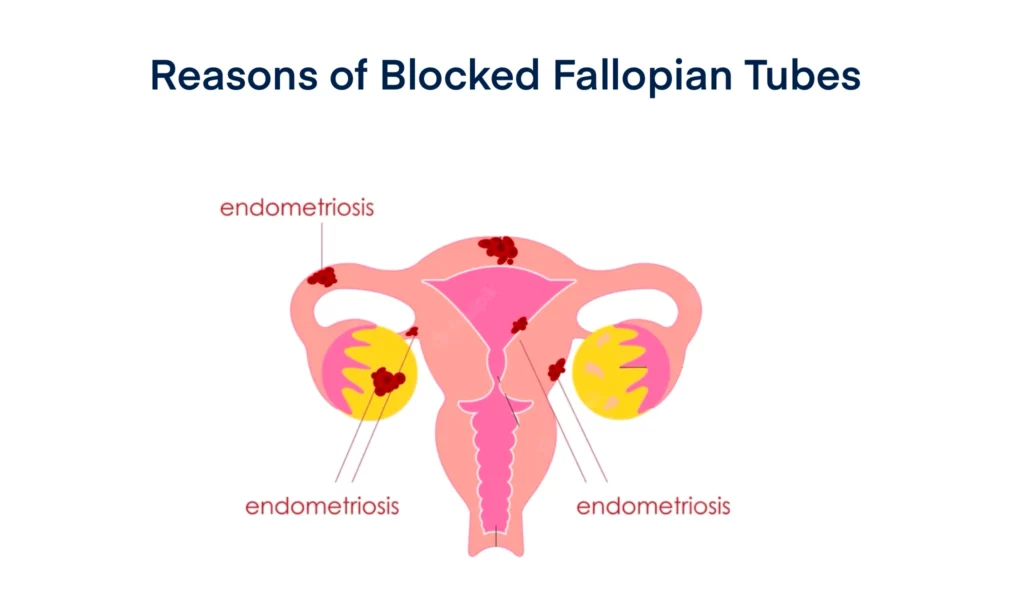
Any scarring, infection or adhesion around the fallopian tube area can cause the fallopian tube to become damaged and eventually blocked. Some common conditions that can trigger such tubal scarring, adhesion or infection include:
- Endometriosis: Endometriosis is an abnormal growth of endometrium tissue outside the uterus causing severe pelvic and abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding. The severe symptoms associated with endometriosis can cause scarring in the fallopian tubes, leading to blockage.
- Uterine fibroids: Also known as uterine myoma, abnormal growth of multiple tissues in the uterus causing severe vaginal bleeding and pelvic pain. These symptoms can also cause tubal scarring and lead to blockage.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID): It is a type of infection in the fallopian tubes, ovaries and/or uterus. PID can cause scarring and fluid development that also increase the risk of fallopian tube blockage.
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs): Gonorrhea and chlamydia are two most common STIs that cause scarring and increase the risk of having blocked fallopian tubes.
- History of ectopic pregnancy: Ectopic pregnancy is a pregnancy that cannot sustain healthily because the fertilized egg abnormally implants outside the uterus. This often causes scarring in the fallopian tubes, leading to blockage.
- History of abdominal surgery: If you have had a fallopian tube surgery in the past, it has a high risk of causing adhesion that blocks the fallopian tubes.
All these conditions are responsible for affecting the fallopian tube area directly and causing the scarring, infection or adhesion that lead to blockage. However most of these conditions cannot be prevented, the risk of STIs can be reduced by using protection during intercourse.
Effect of Fallopian Tube Blockage on Fertility
A female’s ability to conceive and sustain a pregnancy majorly depends on the ovaries, fallopian tubes and the uterus. If a female has a problem in any of these organs, it is likely that the female might have trouble with her fertility.
Fallopian tube is where fertilization actually takes place. Once fertilization occurs, the fertilized egg travels through these fallopian tubes, to the uterus where they implant and further grow. Therefore, if there is blockage in one or both fallopian tubes, it gets you at a high risk of infertility.
If your both fallopian tubes are blocked, you could not become pregnant. If your fallopian tubes are partially blocked, you might get pregnant, but with a risk of ectopic pregnancy. However, if one of your fallopian tubes is healthy, you can have a healthy pregnancy because the egg can travel through the healthy tube.
Diagnosis of Blocked Fallopian Tubes
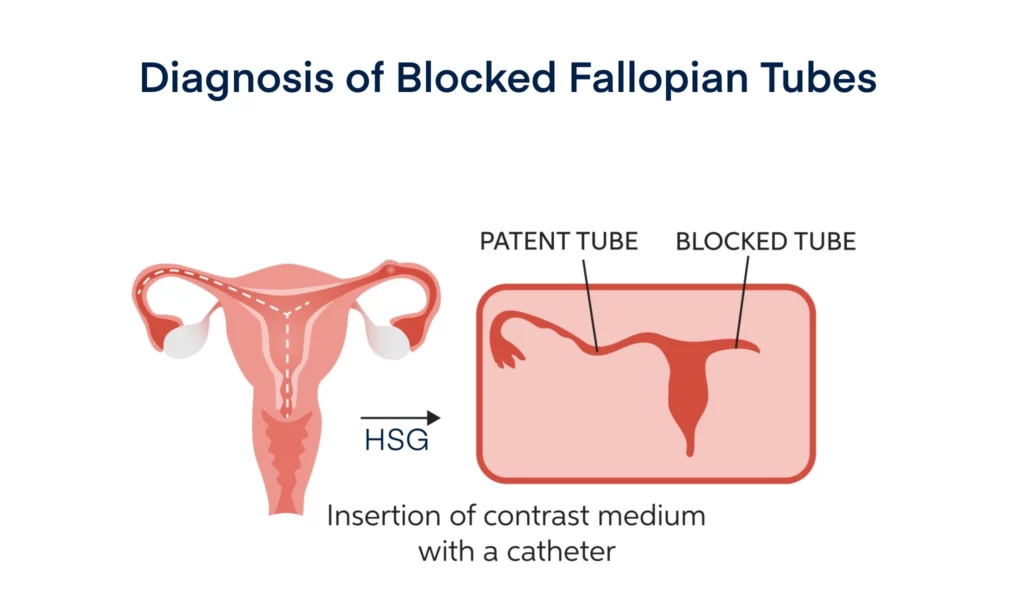
Common fallopian tube blockage tests that identify the condition include:
- Hysterosalpingogram (HSG): HSG is a type of x-ray that involves the use of an that is injected into the womb and an x-ray scan is taken. A uterine tube is considered blocked if the dye cannot make it through.
- Sonohysterogram: Sonohysterogram is a type of ultrasound which uses the same approach of HSG x-ray but uses ultrasound as a mode of imaging the state of fallopian tubes.
- Laparoscopy: Laparoscopy is an imaging technology which requires insertion of a miniature camera through a small cut inside the womb. The camera is then used for taking detailed images of the uterine tubes, to check for the blockage. Doctors do not usually go for laparoscopy as the first option. A doctor may request a laparoscopy test only if needed, depending on the patient’s medical history.
Available Treatments

Fallopian tube blockage treatment without surgery is not possible. However, laparoscopy, otherwise called the keyhole surgery, is an effective treatment for opening the blockage in the fallopian tubes.
A doctor can treat a blocked fallopian tube with laparoscopy surgery in the following ways:
- Removing the scar tissue
- Removing the damage
However, if scarring, adhesions or damage is severe, treating the blockage may not be possible. Still, in case of minor blockage or damage, a doctor can use laparoscopy to remove these minor scar tissues or remove the damage.
Is It Possible to Get Pregnant with Blocked Fallopian Tubes?

The short answer is, yes. You can get pregnant while having partially blocked fallopian tubes, or if one of the tubes is healthy. But, in case of a complete blockage in fallopian tubes, a natural pregnancy is not possible.
Moreover, in case of partially blocked fallopian tubes, a pregnancy can still occur but cannot sustain. It is because partially blocked tubes have a high risk of resulting in an ectopic pregnancy. And, since an ectopic pregnancy implants outside the uterus, in a fallopian tube, the pregnancy cannot sustain and often lead to life-threatening side effects.
Achieving a healthy pregnancy is however possible even if you have blocked fallopian tubes, with the help of in-vitro fertilization (IVF) assisted pregnancy.
Getting Pregnant with IVF

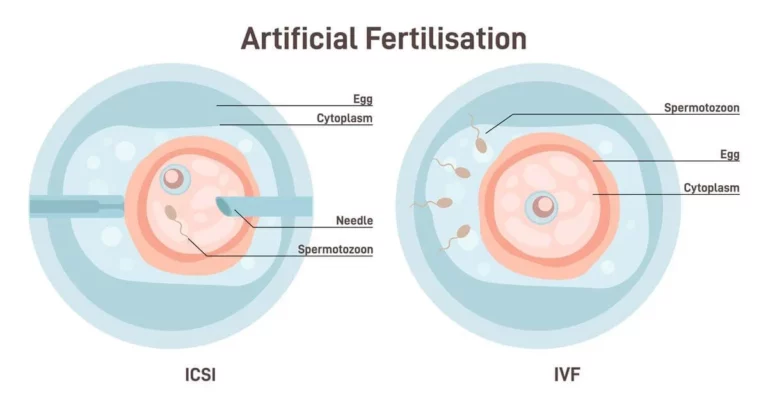
IVF is one of the effective assisted reproductive technologies (ARTs). When a couple experience trouble conceiving for quite a long time, usually more than a year, ARTs help them conceive by assisting the conception process.
In IVF, fertilization does not involve fallopian tubes at all, it takes place in the doctor’s facility. The mature egg is collected as the woman releases it in her ovaries. Then the collected egg is fertilized with the male partner’s sperm, and once the fertilized egg is incubated and grown into a blastocyst (a healthy embryo), it is transferred back to the woman’s uterus.
How does IVF really help a woman with unhealthy uterine tubes get pregnant? IVF does not require the involvement of fallopian tubes. Since fertilization takes place outside the woman’s fallopian tube, it does not concern your pregnancy if you have blocked uterine tubes.
You can always visit a IVF specialist to get pregnant while having fallopian tube blockage, through IVF.
The Bottom Line

Fallopian tube blockage is one of the prominent causes of fertility complications. Because fallopian tubes are a place where fertilization takes place and through which a fertilized egg travels to the uterus, having a problem with these tubes can cause you trouble getting pregnant. Usually, a scarring, adhesion or infection causes such blockage, and considering a treatment may be required if the associated side effects become severe and persist.
And, if you are planning to conceive, seeking IVF treatment may be required because pregnancy is possible while having blocked fallopian tubes, but at a high risk of encountering an ectopic pregnancy. All you need is, seeking help from a fertility specialist who could diagnose your condition and propose a tailored treatment.